Introduction
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution, as applied to the origin of species, is assumed to be a fact rather than a theory in much of American society. We are taught in grade schools, high school, college, nature television programs, and other mainstream media that primitive life emerged from primordial soup billions of years ago, and then that primitive life evolved into the many species of animals that inhabit the world we currently inhabit. And generally, this evolutionary mindset also teaches that man is just another “animal”. Religious beliefs, particularly those professing creation by an all-powerful God with man created in God’s image to rule over the animals, are often relegated to myth status since they require faith rather than being based entirely on natural science. But are Darwin’s Theory of Evolution and current theories on the origin of life based entirely on fact? Or are they just theories that perhaps require a bit of faith as well? This paper explores these questions.
Where and How did Life Begin?
Primordial Soup & The Miller Spark Chamber Experiment – this experiment is featured in nearly every college biology text as evidence for a spontaneous appearance of life, even though both assumptions made and conclusions reached have significant flaws. The setup for this very simple experiment is shown below.
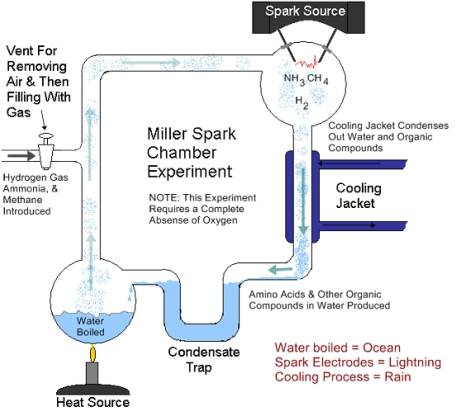
The amino acids produced in the Miller experiment were said to be “building blocks” of life, since proteins, after all, consist of chains of amino acids. The spark source was said to simulate lightning, the cooling produced by the corresponding rain.
Here are the problems with the assumptions incorporated by Miller Spark Chamber Experiment and the conclusions reached:
- Oxygen is assumed to be absent from some primitive atmosphere that is simulated in this oxygen-free experiment. Any oxygen present would prevent the creation of the organic compounds formed in the experiment. Such an atmosphere devoid of “free oxygen” is known as a “reducing atmosphere”. In his Dr. Steven A Austin’s article, Did the early earth have a reducing atmosphere? 1 it is stated that reducing evidence has not been documented in the rocks.”. Furthermore, Dr. Austin disputes the evolutionist theory that banded iron formations proved that little free oxygen was available.
- The ammonia and methane were not there! In his book Creation Facts of Life 2, Dr. Gary Parker states that “Methane (CH4) and ammonia (NH3), two prime gases in the Miller spark chamber, could not have been present in large amounts. The ammonia would be dissolved in the oceans, and the methane should be found stuck to ancient (deep) sedimentary clays. It’s not there!” Furthermore, even evolutionists are starting to abandon the premise that an atmosphere and conditions were at one time correct. As stated in Science News “Research has since drawn Miller's hypothetical atmosphere into question, causing many scientists to doubt the relevance of his findings.”3
- The wrong types of amino acids are produced. According to Dr. Gary Parker 4, the end result, amino acids, were of equal amounts of both short left-handed and long right-handed types. Just one long right-handed amino acid inserted into a chain of short, left-handed amino acids would prevent the coiling and folding necessary for proper protein function.
- A few amino acids is a long ways from creation of life! As you continue reading, you will see that the jump from the amino acid building blocks (assuming you had all of the needed type, which Miller-Urey does not produce) to DNA, proteins, and a living cell is analogous to a expecting a pile of lumber to construct itself into a mansion.
- The experiment does not replicate a natural process. As can be seen in the sketch showing this experiment, the organic compounds are trapped. In addition the trap saves the organic compounds from destruction by the electric charge. This is a “designed” procedure used by organic chemists to increase yields.4
Have Scientists Ever Created Life in a Laboratory? Answer: No.
In 2010, Dr Craig Venter, a geneticist, and his team have managed to make a completely new "synthetic" life form, as they called it. They manufactured a new chromosome from artificial DNA in a test tube, then transferred it into an empty cell and watched it multiply. So, many in the media hailed this as the creation of life. However spectacular this result was, it required already present host cells. In the article, Did Venter create life? Not really say experts, the author states “though the cell's control station is artificial, the cell itself isn't. But it's not a creation of synthetic life...Creation of synthetic life would be to make an entire bacterial cell through chemicals."5
What is Needed to Create Life? In all living things, proteins are intricately constructed from combinations of up to 20 amino through a process involving DNA, or in some viruses RNA. DNA, on the other hand is made and maintained by the proteins of the cell, thus creating a “Chicken & Egg” dilemma discussed later.6. Perhaps the best analogy of the entire process of creation of proteins is to view this as a factory, as discussed by Dr. James Coppedge 7. The DNA serves as the blueprint, messenger RNA serves as a working copy of the blueprint, the ribosome (as you will read below) serves as the shop foreman, the transfer RNA serves as the workers that bring the amino acid the components to their proper locations to create the finished protein product.
DNA, The Miraculous Molecule!
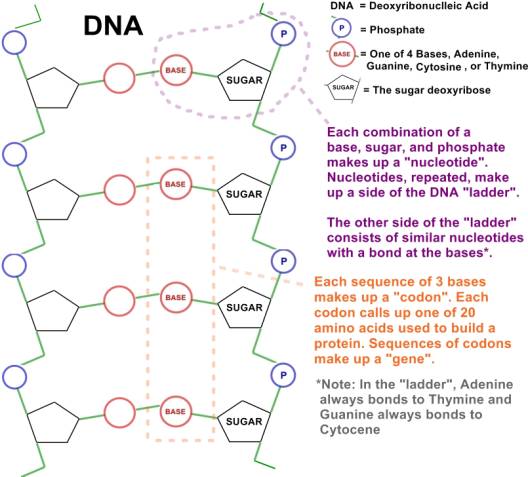
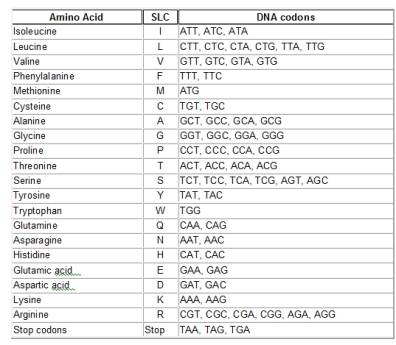
DNA, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetically determined “blueprint” for creating the proteins needed in life-related activities occurring within the cell. DNA consists of a ladder-like molecule where each side consists of repeated units of the sugar deoxyrobose, a phosphate, and one of 4 bases. Each unit is called a nucleotide. The other side of the “ladder” consists of similar nucleotide units, with a bond at the bases. There is a specific pairing up of bases – Adenine always bonds to Thymine, and Guanine always pairs up with Cytosine. Each 3 bases make up what is called a “codon”. A sequence of codons makes up a “gene”. For example, if the first 3 bases of a gene were Adenine, Thymine, and Guanine, we would designate this codon as ATG and it would call up the amino acid Methionine. There are 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 different codons. Each codon (except for one that acts as a signal to stop) will call up one of 20 different amino acids used to build a protein. The DNA structure and how codons are assigned is shown below.
DNA, Then RNA, Then Proteins!
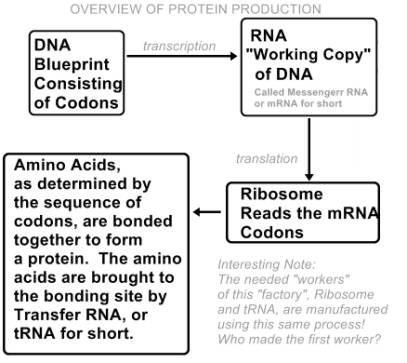
Activator proteins signal the process to begin. As shown in the overview, Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the working copy obtained from the DNA via an unraveling of the DNA “ladder” within a protein complex known as polymerase. mRNA is much like DNA except it only contains one side of the “ladder” and the base Thymine is replaced with Uracil. Also, a slightly different sugar ribose is used in place of the deoxyribose of DNA. The mRNA is processed within the ribosome. The ribosome is the “protein factory”. Within the ribosome, the protein will be built, one amino acid at a time, with transfer RNA (tRNA) bringing the needed amino acids. The sequence of amino acids is then correctly folded into its required three dimensional structure. All of this is summarized nicely in a video shown at http://www.youtube.com/embed/TVkdQhNdzHU and below.
The Book of Life
Each DNA codon (sequence of 3 bases) may be thought of as a word. The words, put together, make up a gene, which we may think of as a sentence. The genes, put together, make up the complete set, the genome. We may think of the genome as the complete book. Clearly, DNA represents information in a specifically and carefully designed order.
There are about 3 billion base pairs in the human genome!8 This would equal 1 billion codons. If we considered each codon to be a “word” in The Encyclopedia Brittanica, this would be over 22 complete sets! All by chance and evolution?
What are the Chances?
The smallest known living organism is Mycoplasma genitialium, with one smallest genome of any self-replicating organism. It has 470 genes corresponding to proteins that, on average, require a specific sequence of 347 amino acids.9 If we look at the shorter proteins, we will assume a protein consisting of 150 amino acids and find the probability for such a protein being formed by chance alone. Three things need to be correct, as shown below: We need a peptide bond, we need the correct isomer of each amino acid, (left-hand, not right hand), and we need the correct amino acid called for to create a functional protein. There are two possible bonds, but only one is the necessary peptide bond. There are two isomers, but only the left-handed isomer results in the protein chain properly folding into its correct three dimensional structure, and there are 20 possible amino acids. So, for each amino acid, there are 2x2x20 = 80 possibilities. For this protein containing 150 amino acids, this results in 80 x 80 x 80 x . . . x 80 = 80150 different possibilities! This number, converted to scientific notation, is equal to 2.9 x 10285 !
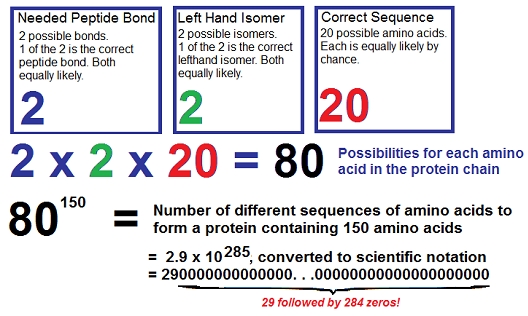
There are many sequences of 150 amino acids that result in a functional protein. In fact, using the ratios given by Doug Axe in his paper, "Estimating the Prevalence of Protein Sequences Adopting Functional Enzyme Folds,"10 and information presented by Stephen Meyer in his book Signature in the Cell: DNA and the Evidence for Intelligent Design.11 , there are approximately 10121 functional sequences for these 150 amino acids, But if we calculate the probability of one of these sequences by obtained by chance alone, we get 10121/80150 = 3.4 x 10-165 = 0.0000…00034 with 164 zeros in front of the 3! And if you double this because there are only 149 peptide bonds needed for these 150 amino acids, this is just a little better than a 1 out of 10164 chance! Considering it is estimated by some that there are about 1050 atoms (total) on earth, the probability of functioning protein made up of 150 amino acids forming by chance alone is essentially zero.
This mathematical improbability has led to many evolutionists to embrace a theory known as Panspermia, where the first life arrived onto the earth from some other life-sustaining planet. This does not explain the origin of life, but merely moves it to another location. Among the evolutionists embracing Panspermia is Francis Crick, the winner of the Nobel Prize for the co-discovery of a double helical structure for DNA 12. Francis Crick stated in his book, Life Itself, that life in all its complexity could not “have arisen by pure chance”.13 Crick also states "An honest man, armed with all the knowledge available to us now, could only state that in some sense, the origin of life appears at the moment to be almost a miracle, so many are the conditions which would have had to have been satisfied to get it going."14
The Chicken and Egg Dilemma of DNA vs. Protein – As described in the previous paragraphs, proteins are formed using a coding mechanism that uses DNA, RNA, tRNA, and mRNA. But, DNA itself requires proteins in order to be formed. As stated by Dr. Stephen C. Meyer, “The cell needs proteins to process and express the information in DNA in order to build proteins”15. So DNA needs enzymatic proteins to function and proteins need the information-storage ability of DNA in order to be built. This logical (and scientific) dilemma forced evolutionists to propose another model for the first protein formation, The RNA World.
The RNA World – The RNA World is a model where DNA is not required for protein production, but rather RNA performs both the enzymatic functions of modern proteins and the information-storage function of modern DNA.
The RNA World Problems – Here are some significant problems discussed by Dr. Meyer:
- The chemical molecules that make up RNA, such as sugars and bases, are difficult to synthesize but are easy to destroy in realistic conditions of a theoretical “life-less earth” proposed by Miller and Urey.16
- RNA can only perform a small fraction of the thousands of functions proteins must perform.17
RNA World Big Problem – Where Did The First RNA Come From?
The RNA World theory does not explain, at all, how the first self-replicating RNA came into existence. As the National Center for Biotechnology Information states, “Although RNA seems well suited to form the basis for a self-replicating set of biochemical catalysts, it is unlikely that RNA was the first kind of molecule to do so. From a purely chemical standpoint, it is difficult to imagine how long RNA molecules could be formed initially by purely nonenzymatic means”.18 In the Scientific American article A Simpler Origin For Life, Robert Shapiro states “No physical law need be broken for spontaneous RNA formation to happen, but the chances against it are so immense, that the suggestion implies that the non-living world had an innate desire to generate RNA”.19 And in the same article, Shapiro quotes Gerald F. Joyce of the Scripps Research Institute and Leslie Orgel of the Salk Institute stating that the spontaneous appearance of RNA chains on the lifeless Earth “would have been a near miracle."
Conclusions About The Origin of Life on Earth
If we reject the theory that the first life occurred by some random chemical process using non-living matter (abiogenesis) and we do not accept that it was transported to earth from some far away galaxy (panspermia), then where did the first life come from? Scientific evidence alone makes it very reasonable for even an evolutionist to at least consider that a Creator created that first life, either as a primitive form of life that evolved into the species we now see, or as fully formed species, some of which are now extinct. This leads to the next topic – The Origin of Species.
The Origin of Species & Problems With Classic Evolution Theory
Classic Evolution Theory Defined
Classic Evolution Theory is largely based on Charles Darwin’s work and writings, primarily his book Origin of Species, originally published in 1859.
There are two types of evolution: microevolution, and macroevolution. Microevolution is evolution on a small scale, within a population. Microevolution can be observed in the fine-tuning of show dog or livestock species characteristics achieved by selective breeding within the species. Macroevolution, on the other hand, involves evolution beyond the species level. According to evolutionists, genetic mutations, genetic drift, migration, and natural selection, over billions of years, are said to account for this macroevolution process 20. We accept microevolution, since it is observable in agriculture and even in nature. For example, in whitetail deer populations, bigger deer, with their larger mass to surface area ratio and ability to eat winter browse at greater heights, survive cold harsh winters better than smaller deer, thus resulting in bigger deer in cold northern climates.21 Macroevolution, however, is what we take issue with in this paper. All future references in this paper to evolution should be assumed to be speaking of macroevolution.
Intermediate Fossils – Where are They? – Charles Darwin himself proclaimed “the distinctness of specific forms, and their not being blended together by innumerable transitional links, is a very obvious difficulty....” 22
Yet, evolutionist David Raup, curator of the Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago, which houses 20 percent of all fossils known, states "we are now about 120 years after Darwin, and knowledge of the fossil record has been greatly expanded ... ironically, we have even fewer examples of evolutionary transition than we had in Darwin's time." 23
Homologies, The Circumstantial Evidence of Evolution – Homology, as used in the Theory of Evolution, refers to the similarity of structures. For example, you will typically see a sketch like that shown below in a college biology text, showing similarity of a whale’s flipper, a bat’s wing, and a human hand.
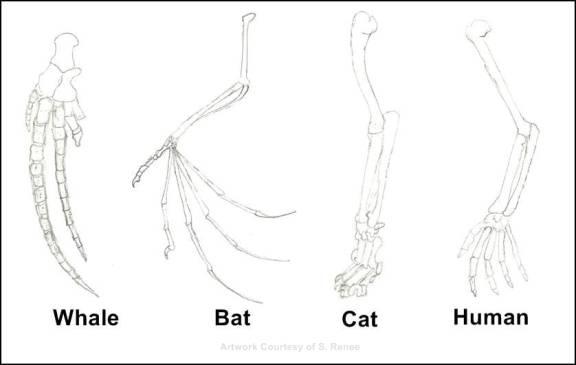
To the student being taught evolution in the college classroom, these homologies seem to serve as evidence. But homologies do not prove a thing. In fact, if one looks deeper into the issues, as molecular biologist Michael Denton does in his book Evolution: A Theory in Crisis 24, one tends to see homologies as proof against evolution rather than for it. In Denton’s book, he shows in repeated examples that homologies can not be traced back to similar processes and events in the development and growth of the embryo. Also Denton describes how the homologous structures lack a common genetic correspondence. In summary, the similar structures come about in very different manners – thus the common appearances become nothing more than “circumstantial evidence” that does not hold up under closer inspection – Denton makes a reference as such in his book. Some, such as biologist Gary Parker, even cite homologies as “creation according to a common plan” 25. In other words, the homologies suggest a common designer.
Fossils, Evolution, and Artist’s Renditions - A sketch similar to the one below will usually be featured in college biology text books as evidence of an evolutionary progression of intermediates from land mammal to whale.
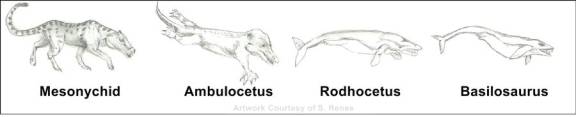
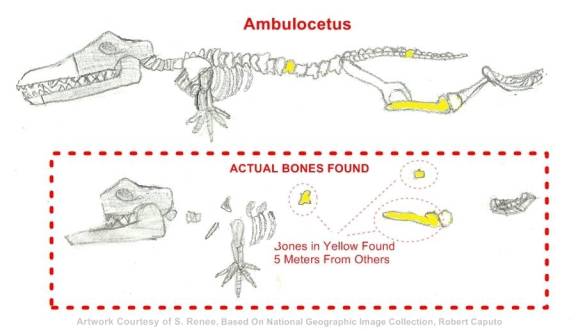
What is not mentioned, however, is that the form of Ambulocetus, the supposed intermediate between whale and land mammal, was constructed from a small number of bones (shown below), with several being found 5 meters from the others. The webbing in the feet was the work of an artist and the long tail was also added by an artist based on the assumption that it was a whale ancestor 26 (circular reasoning). The sketches shown above were redrawn based on common sketches typically displayed in biology text books.
Another problem with Ambulocetus is that the skeleton pieces were found in geologic strata at or above where whales were found, as opposed to being found below. An assumed evolutionary ancestor of the whales should be found in geologic strata below the whales.27
The Cambrian Explosion, And Its Implications - Evolutionists will often cite “geological” evidence for evolution, but often they will gloss over the very serious discrepancy known as the “Cambrian explosion”. What this refers to is the sudden occurrence of species, many of which we can still see today. There were jellyfish, sea urchins, nautiloids (squid-like animals), star fish, and clams, some with complex biological structures. And they have no “evolutionary ancestors” in the Pre-Cambrian geological column below. As stated in the documentary Darwin’s Dilemma, “There is a geologically-sudden appearance of dozens of major complex animal types in the fossil record without any trace of the gradual transitional steps Charles Darwin had predicted.” 28 To further compound evolutionary claims that Precambrian animals were too soft to be fossilized, Darwins Dilemma documents recent finds in China of very soft bodied embryos just below the Cambrian layer, yet we find no evolutionary ancestors of hard shelled trilobites (which are notorious for leaving many fossils) of the Cambrian layer. In short these findings indicate that Darwin’s “Tree of Life” (where all species branch off from a common ancestor) looks more like many thousands of individual blades of grass growing in one’s front yard!
As paleontologist Stephen J. Gould stated "The fossil record had caused Darwin more grief than joy. Nothing distressed him more than the Cambrian explosion, the coincident appearance of almost all complex organic designs..." 29
Genetic Mutations? Genetic mutations consist of changes in DNA replication that usually result in a defect. But the result of these mutations is a net loss of genetic information! In short, “birth defects”! Lee Spetner, Physicist from MIT, Gary Parker, Biologist from Ball State University, and others have stated that genetic mutations that add information are not observed 30 and are improbable to the point of being virtually impossible 31. A much touted example of a beneficial mutation is the sickle cell defect that provides immunity to malaria – but this mutation, like others, results in a 25% mortality rate from the sickle cell anemia alone, and another 25% mortality rate for those that it does not protect from malaria. And for survivors come all the other adverse conditions of the sickle cell anemia itself 32. This is hardly an evolutionary step up! Michael Behe wrote about studies on E. coli bacteria being raised in the laboratory, duplicated about 7 times a day, grown continuously for over 30,000 generations, which would be equivalent to about a million human-years. The “evolutionary” result of these mutations has been, as Behe puts it, “mostly de-evolution . . . with the bacterium throwing away chunks of its genetic patrimony, including the ability to make some of the building blocks of RNA” 33.
In short, evidence suggests that genetic mutations result in demise, defects, and de-evolution. In fact, in 1980, evolution experts from throughout the world gathered at a conference in Chicago titled “Macroevolution” to answer to the question: Can the genetic mutation mechanisms that allow for microevolution (within a species) be used to explain evolution of one species into another? The answer was: “At the risk of doing violence to the positions of some of the people at the meeting, the answer can be given as a clear No.” 34
It should be clear that the theory of evolution, as an explanation of the origin of species is only a theory, not a scientific fact, even for those that who do not believe in an all-powerful creator.
Science of the Natural vs. Science of the Supernatural
Science of the Natural - The previous information in this document uses the Science of the Natural World in its arguments against the theory of evolution as an explanation for the origin of life and the origin of species. Current phenomena and processes, such as building blocks of the first life, genetic mutations, and diversity of species were examined and accepted scientific principles were applied. So far, in this document, no arguments or principles that assume an all-powerful Creator were made nor were assumptions about the past such as a supernaturally orchestrated world wide flood causing geological fossils to be deposited in a catastrophic manner or an all-powerful creator designing and creating living matter assumed. In much of the remainder of this document, we examine what I call The Science of the Supernatural.
Science of the Supernatural & Faith – The science of the supernatural assumes a Creator that created matter from nothing (creatio ex nihilo). Although this seems a fantastic claim to a secular scientist studying this natural world, the only other conclusion one may reach if one rejects evolutionary theories of a primordial soup organizing itself into complex life-producing systems is that aliens or space debris brought life to this earth (panspermia). And this latter claim of panspermia seems to me even more fantastic, yet some evolutionists have adopted that latter theory. Furthermore, the limitations of genetic mutations to produce macroevolution of one distinct species to another and the lacking fossil evidence showing a gradual transition of one distinct species to another gives one reason to believe in the only alternative for an explanation of the diversity of species – an all-powerful Creator. And many scientists holding advanced degrees from secular universities have come to this conclusion – see Appendix D.
Once an All-Powerful Creator is Assumed, one has no problem believing that Jesus Christ fed 5000 people by creating food (matter) from nothing or created live cells from dead cells when He raised the dead (and rotting) corpse of Lazurus to life. Also, with an all-powerful Creator assumed, one may believe that the Genesis account of the flood also occurred. And there is much evidence for the authenticity of the Bible itself, such as many fulfilled, detailed, prophecies and archeological evidence – for some good resources, read Evidence That Demands a Verdict by Josh McDowell and also The Evidence Bible by Ray Comfort, and http://www.faithfacts.org/search-for-truth/maps/archaeological-and-external-evidence , just to name a few.
The Genesis Flood and its Implications - The Genesis flood should be classified as a supernatural event, since it was divinely predicted and involved incredible logistics in the building of the Ark, procurement of the animals, survival at sea, and redistribution of species. With this assumption of the Genesis Flood, many creationists have proposed explanations for what we observe in the fossil record, the geological column, and radiometric dating.
- The Geological Record is better Represented by the Catastrophic Flood Model than the conventional Uniformitarian Model – The Uniformitarian model, widely taught in secular schools and universities, assumes a gradual depositing of the geological layers over millions of years. The Catastrophic flood model, assumes sudden and severe depositing of geological layers in very short time spans. Whitcomb and Morris address the shortcomings of the Uniformitarian Model in great detail in their book, The Genesis Flood 35.
- Catastrophic Sediment Deposits Explain The Cambrian Explosion – The Cambrian Explosion, with the sudden and unexplained abundance of species amounting to as much as 100 million radiometric years (according to evolutionists), is explained by the sudden catastrophic Genesis flood event. In addition, lack of fossils in the Precambrian layer is explained by the initial violent nature of the flood, where, according to Genesis 7:11 “fountains of the great deep were broken up”. 36
- The Genesis Flood Explains Sudden Mountains and Tectonic Movement – The mountains we see today appear to be formed in a relatively short period of time. Using the Genesis Flood model, the uplift would occur in a relatively short amount of time after the flood.37
- Radiometric Decay Rates May Have Been Affected – Some have theorized that the conditions prior to the flood affected radiometric decay rates. 38 Radiometric dating methods use the concept shown below, where assumed amounts of radioactive parent and resulting daughter (product of radioactive decay) are assigned to the material measured. Then a comparison of present day amounts, coupled with a half life that is assumed to not have changed, combined with an assumption of a closed system, are all used to calculate an age of the material. The half-life method measures how much of the parent isotope has converted into the daughter isotope and then calculates an age based on that amount. The figure below gives a simplified example – since half of the parent isotope was converted to the daughter isotope, and the half-life is assumed (in this example) to be 1500 years, we conclude that the substance measured is 1500 years old. The half-life of Carbon-14 is about 5730 years and carbon-dating has in fact been shown to be fairly accurate for dating historically verified artifacts of a few thousand years in age. Other half-lives like that of Potassium-40 have extremely large half lives of billions of years. Potassium-40 has a half life of 1.3 billion years.
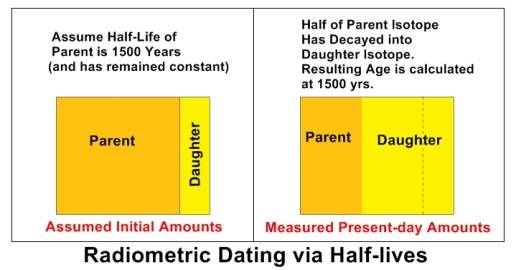
Addressing Radiometric Decay – The process of radiometric dating, applied in a naturalistic and scientific manner (no supernatural intervention) assumes no previous decay of parent into daughter product initially. What is not considered, however, is that in the Genesis account of our creation, God created the world in full form and process, as stated by Henry M. Morris in both his books Scientific Creationism 39 and The Genesis Flood 40. Man, as created by God, was not created an infant, trees and grass were not created as seeds, etc. Likewise, the mountains, rock, rivers, etc. were created in full pre-flood form as well. It is not unreasonable to assume that ratios of parent to daughter products measured in rocks with radiometric isotopes of very large half lives were very similar at the time of creation to what is found today. Kurt Wise, in Faith, Form, and Time explains that in the original creation (not evolution), fruit trees would have to be created already with fruit, soil would already have to be created with nutrients from the products of decomposition.41 Thus, if one were to have done radiometric dating in the times of Adam, they would conclude the earth was already billions of years old since much of the daughter product was already present! In addition, the light of the stars light years away would already be visible at the time of Adam. And if this is the case (as I believe it is), it is likely that no amount of scientific study by either creationist or evolutionist using the science of the natural will prove or disprove this assertion.
The Most Important Conclusion
Once an all-powerful Creator is assumed to be able to create matter instantly, as was done in the feeding of the 5000, one has no problem believing that the world we live in could be created in 6 days, 6 minutes, or 6 milliseconds. In addition, when one embraces the complete bible, including all of Genesis in its literal translation, one then has the needed foundation for all other teachings. Genesis passages are mentioned by Jesus himself as well as the Apostle Paul and other New Testament writers. And perhaps most importantly, Original Sin, and its immense consequences, is documented in Genesis.42 The remedy for that Original Sin, along with hope for life in this world and the eternal afterlife lies in faith in Jesus Christ.43
Which Path of Faith Will You Choose?
Naturalistic science alone can only take us so far in understanding the origin of life and the answers to the much deeper questions such as “What is my purpose in this life ?” At some point, the individual needs to place their faith in science or a creator. One must believe in the latest scientific theory alone accounting for and explaining the incredible complexity, splendor, and diversity of life as we observe, or one must believe in the role of a Creator. As world-renowned neurosurgeon Ben Carson put it, “Can you prove evolution? No. Can you prove creation? No. Can you use the intellect God has given you to decide whether something is logical or illogical? Yes, absolutely. It all comes down to "faith"--and I don't have enough to believe in evolution.” 44 Many would argue that you may believe in both a creator and evolution, but can you? If you can not believe in “creation from nothing”, as described in Genesis and in the Gospels where Jesus created bread and fish to feed 5000, what other creation is there?
Appendix A – References
1. Steven A. Austin, Did the Early Earth Have a Reducing Atmosphere , http://www.icr.org/article/did-early-earth-have-reducing-atmosphere/ .
2. Gary Parker, Creation Facts of Life, (Green Forest, AR: Master Books, 1980) p.25.
3. S. Simpson, Life’s First Scalding Steps, http://www.sciencenews.org/sn_arc99/1_9_99/bob1.htm .
4. Gary Parker, Creation Facts of Life, p.26.
5. Times of India, Did Venter create life? Not really, say experts, http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2010-05-24/science/28301741_1_genome-synthetic-life-j-craig-venter
6. Sean D. Pittman, M.D. The Chicken or the Egg, DNA or Protein? http://www.detectingdesign.com/abiogenesis.html .
7. James E. Coppedge, Evolution: Possible or Impossible? (Zondervan Publishing House, 1973) p.139.
8. John Markoff, 44 Million Words Strong Britannica to Join Internet http://www.nytimes.com/1994/02/08/business/44-million-words-strong-britannica-to-join-internet.html (Feb 1, 2012)
9. John F. Ashton, In Six Days: Why 50 Scientists Choose To Believe in Creation, Master Books, 2000, p.139
10. Douglas D. Axe, "Estimating the Prevalence of Protein Sequences Adopting Functional Enzyme Folds," Journal of Molecular Biology (2004).
11. Stephen C. Meyer, Signature in the Cell: DNA and the Evidence for Intelligent Design, HarperOne; (2010), p.212
12. Panspermia and the Origin of Life on Earth, http://www.panspermia-theory.com/
13. Francis Crick, Life Itself, Its Origin and Nature (New York: Simon and Schuster, 1981) p.52-55
14. Francis Crick, Life Itself, Its Origin and Nature, p.88
15. Stephen C. Meyer, Signature in the Cell, p.134
16. Stephen C. Meyer, Signature in the Cell, p.301
17. Stephen C. Meyer, Signature in the Cell, p.304
18. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. New York: Garland Science; 2002. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26876/
19. Robert Shapiro, A Simpler Origin of Life, http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=B7AABF35-E7F2-99DF-309B8CEF02B5C4D7&page=4
20. http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_01
21. http://www.mainedeerhunting.com/about_trophy_buck_hunting.html
22. Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species, Forgotten Books, 2007, p.265
23 David Raup, "Conflicts Between Darwin and Paleontology", Field Museum of Natural History Bulletin, Vol. 50 (1) (1979).
24. Michael Denton, Evolution: a Theory in Crisis, Adler & Adler, 1986, p.142-155
25. Gary Parker, Creation Facts of Life, p.45
26. Don Batton, A Whale of a Tale, http://creation.com/a-whale-of-a-tale
27. Angela Meyer, The World of Whales, http://www.answersingenesis.org/articles/cm/v19/n1/world-of-whales
28. Darwin’s Dilemma, Illustra Meda 2009, http://www.darwinsdilemma.org/
29. Gould, Stephen J., The Panda's Thumb, (1980), p. 238-239
30. Gary Parker, Creation Facts of Life, P. 122
31. Lee Spetner, Not by Chance!, Judaica Press (1999) , p. 131-138
32. Gary Parker, Creation Facts of Life, p. 117
33. Michael Behe, The Edge of Evolution, (Free Press: Simon and Shuster, 2007) p. 16
34. Evolutionary Theory Under Fire, Science Magazine, summary of 1980 Chicago Conference on Evolution. Extract found at http://www.sciencemag.org/content/210/4472/883.extract?sid=c7069ec8-d7b1-4c17-a38c-65d95fca611f
35. Dr. Henry M. Morris, The Genesis Flood, 50th Anniversary Edition (Presbyterian and Reformed Publishing Company, 2011)
36. Kurt Wise, Life’s Unexpected Explosion, Answers in Genesis, http://www.answersingenesis.org/articles/am/v5/n1/life-explosion
37. John Baumgardner, Recent Rapid Uplift of Today’s Mountains, Institute for Creation Research, http://www.icr.org/article/98/
38. Dr. Don DeYoung, Thousands, Not Billions, (Master Books, 2005)
39. Dr. Henry M. Morris, Scientific Creationism, (Master Books, 2000) p. 209
40. The Genesis Flood, 50th Anniversary Edition, p. 237
41. Kurt P. Wise, Faith, Form, and Time, P.63
42. Russel Grigg, What does the New Testament Say About Creation?, Creation Ministries International, http://creation.com/new-testament-creation
43. Campus Crusade For Christ, The Four Spiritual Laws, http://www.campuscrusade.com/fourlawseng.htm
44. Evolution? No. “I Don’t Have Enough Faith”, Interview with Ben Carson, Adventist Review, http://www.adventistreview.org/2004-1509/story2.html
Appendix B – Recommended Resources
Creation Facts of Life by Gary Parker, Master Books, also available online at
http://www.answersingenesis.org/articles/cfl/beginning-at-beginning - this was one of the best books I read that examined flaws in the theory of evolution, written by a former evolutionist and university biology professor
In Six Days: Why Fifty Scientists Choose To Believe in Creation by John Ashton, Master Books, 2001 – This is a great book to cite when some evolutionist proclaims that belief in Creation is only for the uneducated!
Signature in the Cell: DNA and the Evidence For Intelligent Design, by Stephen Meyer, Harper One, 2009 – Cutting edge scientific evidence for a Creator!
The Intelligent Design Collection (DVD) - Darwin's Dilemma, The Privileged Planet, Unlocking the Mystery of Life– Illustra Media, 2010 – This 3-DVD set deals with the miracle of life and DNA, the unlikehood of another life-bearing planet, and geological mystery that evolutionists can not explain. Very well done!
Icons of Evolution – Dismantling the Myths DVD, Focus on the Family – this is a well-done, well-documented documentary
Explore Evolution: The Arguments For and Against Neo-Darwinism By: Stephen C. Meyer, Scott Minnich, Jonathan Moneymaker, Paul Nelson & Ralph Seelke, Hill House Publishers, London & Melbourne (2007) – a great book for incorporation into a public school curriculum! See http://www.exploreevolution.com/ for more details.
Websites
http://creation.com/
http://creationsafaris.com/epoi_toc.htm
http://www.allaboutscience.org/
http://www.answersingenesis.org
http://icr.org
Appendix C – About Many of the Cited Authors
Steven A. Austin - B.S. (Geology), University of Washington, Seattle, WA,1970, M.S. (Geology), San Jose State University, San Jose, CA, 1971, Ph.D. (Geology), Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, 1979
Gary Parker – B.S. (Biology/Chemistry), Ball State University, M.S. Biology/Physiology), Ball State University, Ed.D. (Biology/Geology), Ball State University. Interestingly enough, Dr. Parker taught biology from an evolutionist viewpoint for a few years before adopting a creationist view. See http://www.answersingenesis.org/articles/cfl/beginning-at-beginning
Sean D. Pittman, M.D. - Loma Linda University School of Medicine, 1993 – 1997, Major, United States Army, active duty 1997 – 2001, Residency: Pathology, Loma Linda University Medical Center, 2001 – 2005, Fellowship: Hematology, City of Hope National Medical Center, 2005 - 2006
James E. Coppedge – B.A., B.D., Ph.D., former director of the Center for Probability Research in Biology, Northridge, California. Has studied at Asbury College and Seminary, Pepperdine University, California Graduate School of Theology, and the University of Southern California
John F. Ashton, Ph.D. - A Chartered Chemist, Fellow of the Royal Australian Chemical Institute, Fellow of the Australian Institute of Food Science and Technology, strategic research manager for the Sanitarium Health Food Company in Australia.
Douglas D. Axe - is the director of Biologic Institute. His research uses both experiments and computer simulations to examine the functional and structural constraints on the evolution of proteins and protein systems. After a Caltech PhD he held postdoctoral and research scientist positions at the University of Cambridge, the Cambridge Medical Research Council Centre, and the Babraham Institute in Cambridge.
Stephen C. Meyer – B.S. degree in Physics and Earth Science, Whitworth College, Ph.D. from University of Cambridge in history and philosophy of science. Dr. Meyer is at the cutting edge of the Intelligent Design movement and is the Director of the Center of Science and Culture at the Discovery Institute.
Francis Crick – B.S. degree in Physics at the University College in London, did research at Cambridge University Winner of Nobel Prize for co-discovery of DNA structure. Did not believe in abiogenesis (life from chemicals) but rather believed the first life arrived from another planet containing life.
Appendix D - Noted Scientists that Believe in a Biblically Based Creation
http://creation.com/creation-scientists – List of over 100 scientists, each having earned a Ph.D. in a science related field.
http://www.answersingenesis.org/home/area/bios/ - a List of 100’s of scientists, most with advanced degrees.
|








